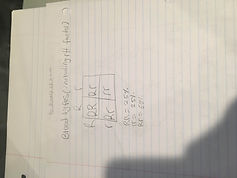Emory Jhonson - Fragile-X Syndrome:
❏ Genotype: FMRP
❏ Phenotype: moderate to severe mental retardation, hyperactivity, macroorchidism, large ears, prominent jaw, and high-pitched, jocular speech.
❏ Homozygous v. Heterozygous: Heterozygous
❏ Dominant v. Recessive: Dominant
❏ Allele: F, M, R, 1
❏ Trait: Mental Retardation
❏ Gene: Mutations in the FMR1 gene cause Fragile X Syndrome
❏ Punnett Square: See Picture Below
❏ Pedigree: See Picture Below
❏ Inheritance Pattern: See Picture Below
❏ Explanations and examples of the following complex inheritance patterns:
❏ Polygenic Inheritance: If a mother is a carrier of Fragile X Syndrome, all of her children are at a 50% risk inheriting Fragile X Syndrome
❏ Incomplete Dominance: Fragile X Syndrome is neither Recessive or Dominant
❏ Codominance: Mutations in the FMR1 Gene cause this disease
❏ Multiple Alleles: Algebraic results for equilibrium allele frequencies are presented for an arbitrary number of alleles, and numerical results are presented for the case of 9 alleles
❏ Environmental Factors: There are no environmental factors in Fragile X Syndrome. The only variable that can determine whether a child will have this disease or not is whether his or her mother is a carrier.
❏ Genotypes of the following:
❏ Common Human Traits (consider the “Making Babies” Project):large ears, prominent jaw, and high-pitched, jocular speech.
❏ Blood Types (including rH factor):See Picture Below
❏ Common Genetic Disorders (we will look at a few in class): causes a range of developmental problems including learning disabilities and cognitive impairment.
❏ Instructions for doing the following:
❏ Determining genotypes and/or phenotypes of parents based on background information or family information (their parents and/or children): Look at the couples in the family. See who originally was the carrier of Fragile X Syndrome (it will be a mother due to the fact that Fragile X Syndrome is an X linked disorder). After you find out where the disorder first started, you can make a punnett square and follow that down until the family stops.
❏ Creation of a Punnett Square using parent background information: Take the alleles from the dad and put them on top of the punnett square. Take the alleles from the mother and put them on the side of the punnett square. Combine the alleles from the mom and dad to create genotype.
❏ Use of Punnett Squares to determine statistical probabilities for offspring inheriting certain traits, and to calculate genotypic/phenotypic ratios: If a mother is a carrier of Fragile X Syndrome her kids are at a 50% chance of inheriting the disorder.
❏ Creation of a Pedigree using family history information: Keep tracing the carriers to the children and so on.